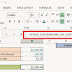
Excel provides great tools to combine or join text/data from multiple cells into one cell. There are primarily two ways in which we can join text using Excel 2013:
- Using Ampersand Operator (&)
- By applying CONCATENATE function
Let's discuss both of these methods with some examples. Say for example we have a client list with "First Name" in column A, "Last Name" in column B and "Age" in column C. We wish to join these text into single cell (say in column D).
1. Using Ampersand Operator (&)
To join text of first name entry in cell A4 with last name in cell B4 and age in cell C4, use the formula below in cell D4 (since we need output data in column D):
=A4&" "&B4&" "&C4 [Output: Tiger Woods 37]
You can add customized text or numbers inside the formula to get desired results. For example,
="Name-"&A4&" "&B4&"; "&"Age-"&C4 [Output: Name-Tiger Woods; Age-37]
Text strings should always be placed using double quotes (eg. "Name-" or " " for space) while the reference cell formula (eg. C4) do not need double quotes. For numbers, using double quotes is optional.
2. By applying CONCATENATE function
The CONCATENATE function in Excel joins upto 255 text/data cells into one text string. We can join text, cell references, number or special characters using this function.
Syntax: CONCATENATE(data1, data2, data3, ....., data255)
- data1: this is the first data/text that needs to be concatenated (required field)
=CONCATENATE("Name-",A4," ",B4,"; ","Age-",C4) [Output: Name-Tiger Woods; Age-37]
CONCATENATE is always preferable for joining text/data of multiple cells since it effective to use and less prone to error.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
Text strings should always be placed using double quotes (eg. "Name-" or " " for space) while the reference cell formula (eg. C4) do not need double quotes. For numbers, using double quotes is optional.