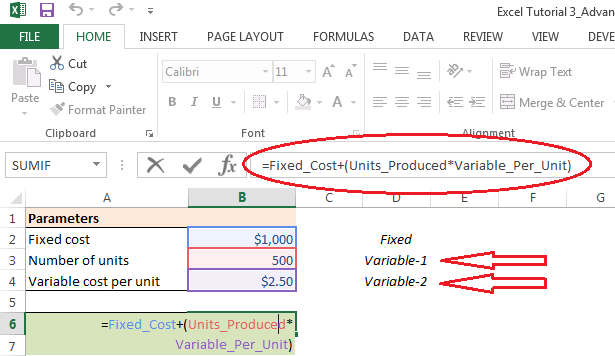
After using Scenario Manager to add scenarios to a table in a worksheet, we can generate a summary report to visualize all the scenarios as well as scenario with current input values. The summary report show input values in different scenarios as well as the output generated (based on the selection).
1. Open the workbook containing the required scenarios.
2. Open the Scenario Manager dialog box.
Go To: “DATA” tab in the ribbon>> What-If Analysis>>>Scenario Manager [Shortcut: Alt+AWS]
3. Click on the "Summary" button in this dialog box.
A new dialog box will open giving the options to generate the summary report. The dialog box gives us choice of reports that can be generated: Scenario summary (static) and Scenario PivotTable report (dynamic).
After selecting the type of report, click on "Result cells" and select the result cell (required output).
4. Click "OK" to generate the report.
Excel creates a separate worksheet with input values along with selected result cells for all the scenarios as well as current input values. We can appropriately rename and re-position this Scenario summary worksheet and then save the workbook.